Electric Drive Train in Electric Vehicle
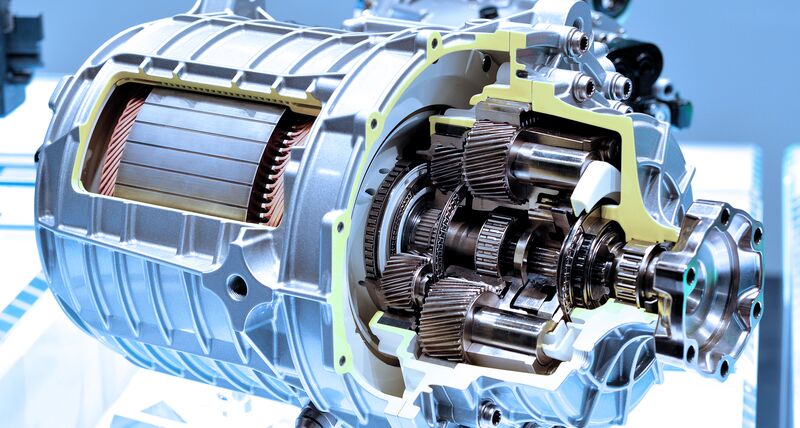
Electric drive trains in EVs are systems that deliver power from the battery to the wheels. They consist of three main components: the electric motor, the drive shafts, and the transmission. The electric motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, the drive shafts transfer the torque from the motor to the wheels, and the transmission adjusts the speed and direction of the rotation. Electric drive trains can have different configurations, such as battery electric vehicles (BEVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), depending on the source and storage of the electrical energy. Electric drive trains have several advantages over internal combustion engine (ICE) drive trains, such as higher efficiency, lower emissions, smoother operation, and regenerative braking.
You are interested in the electric vehicle drive train component, which is the system that delivers power from the battery to the wheels. There are three main components of the electric vehicle drive train: the electric motor, the drive shafts, and the transmission. The electric motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, the drive shafts transfer the torque from the motor to the wheels, and the transmission adjusts the speed and direction of the rotation. Depending on the source and storage of the electrical energy, electric vehicles can have different types of drive trains, such as battery electric vehicles (BEVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
 |
| Electric Drive train & Motor |
Some of the core components of an electric vehicle drive train are :
- Battery Pack: The battery pack is made up of multiple lithium-ion cells and stores the energy needed to run the vehicle. Battery packs provide direct current (DC) output.
- DC-AC Converter: The DC supplied by the battery pack is converted to alternating current (AC) and supplied to the electric motor. This power transfer is managed by a sophisticated motor control mechanism that controls the frequency and magnitude of the voltage supplied to the motor in order to manage the speed and acceleration as per the driver’s instructions.
- Electric Motor: The electric motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, that is delivered to the wheels via a single ratio transmission. Many EVs use motor generators that can perform regeneration as well.
- On-board Charger: The on-board charger converts AC received through the charge port to DC and controls the amount of current flowing into the battery pack.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS continuously monitors the state of the battery and is responsible for taking necessary measures in case of a malfunction. It also helps to optimize the battery lifetime and performance by managing the state of health, state of charge, and cell balancing of the battery.

